In the medical world, chronic pain management is a subject that often sparks an array of complex discussions, particularly in the context of opioid medications. With a well-documented history of addiction, overdose, and other serious side effects, these potent drugs have become a source of concern for both patients and health professionals alike. For this reason, many people are exploring alternative treatment methods that can offer effective pain relief without risking dependency or other health issues. In this article, we will delve into several clinically proven strategies for managing chronic pain without the use of opioids.
Physical Therapy: An Active Approach to Chronic Pain Management
Physical therapy is a common non-opioid treatment method for chronic pain. It involves a series of prescribed exercises and movements designed to alleviate pain, improve physical function, and help patients manage their symptoms on a long-term basis. Physical therapists also provide education on safe movement and activities to prevent injury and reduce pain.
In parallel : Exploring the Benefits of Infrared Saunas: Can They Enhance Your Body”s Detoxification Journey?
Under the guidance of a trained therapist, physical therapy can enhance strength, flexibility, and endurance, which can help in reducing chronic pain. Moreover, it can also address the psychological dimensions of pain by promoting a sense of self-efficacy and autonomy. In many cases, it can provide significant relief without the need for medication.
Integrative Therapies: Holistic Health Care for Chronic Pain
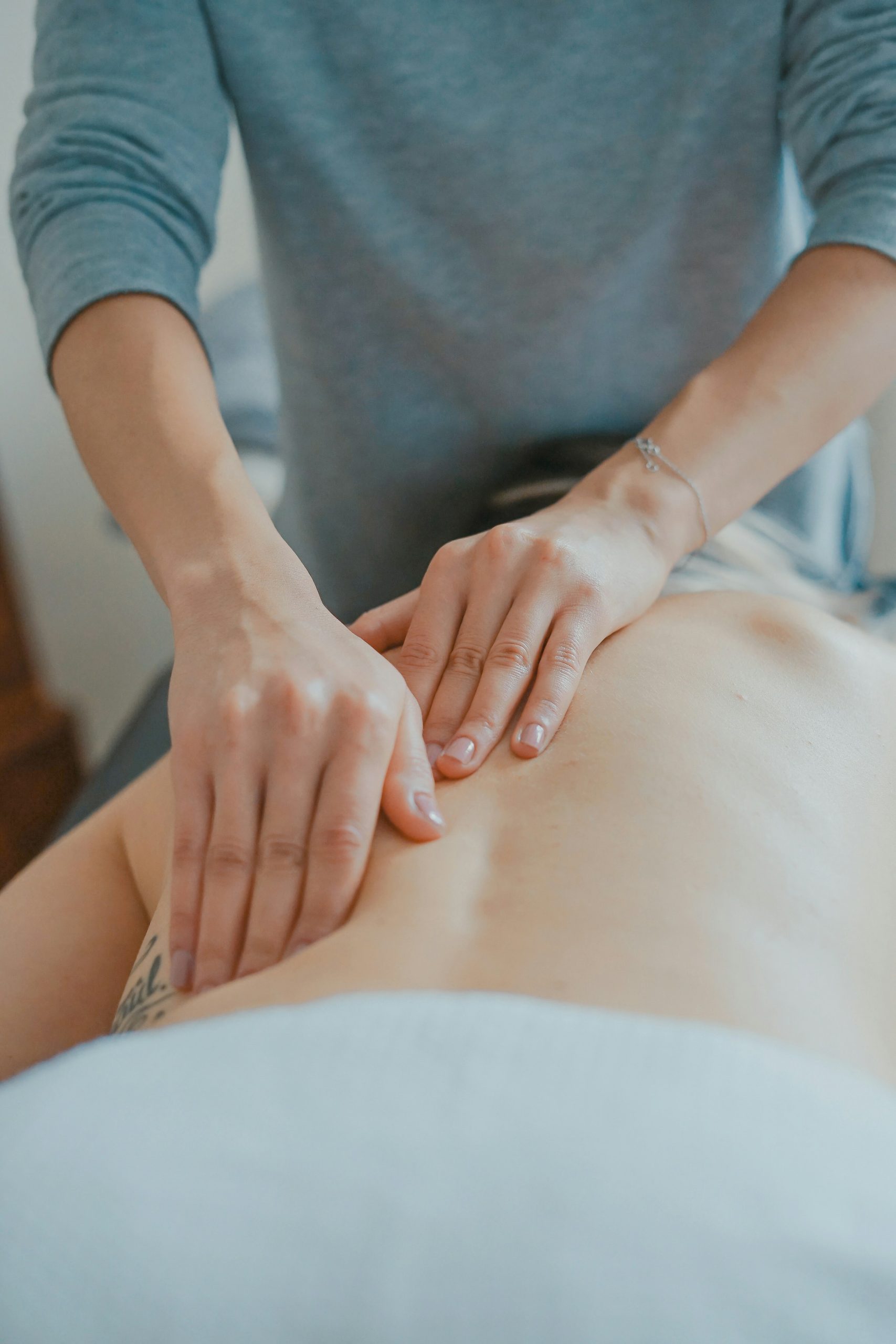
As the name suggests, integrative therapies incorporate a variety of treatment approaches to address the whole person – mind, body, and spirit. They are based on the understanding that chronic pain is not just a physical issue, but can also be influenced by emotional and psychological factors.
Also read : Discover top-rated pharmacies in the uk for your health needs
In this context, therapies such as acupuncture, massage, yoga, and meditation have proven effective in managing chronic pain. Acupuncture, for instance, has a long history of use in traditional Chinese medicine and is believed to stimulate the body’s natural painkillers. Massage therapy can help release tension in the muscles, while yoga and meditation can help manage the emotional and psychological aspects of chronic pain.
In addition, dietary modifications and nutritional supplements could also play a role in pain management. An anti-inflammatory diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, might help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
Psychological Interventions: The Power of the Mind in Pain Management
The role of psychological factors in the experience of chronic pain has been well-documented in medical literature. As such, psychological interventions have become an integral part of chronic pain management.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one such evidence-based psychological approach. It helps patients change negative thought patterns and behaviors that can exacerbate pain. CBT can help patients develop healthier coping mechanisms, improve emotional regulation, and reduce pain intensity.
In addition to CBT, other psychological therapies, such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), can also help in managing chronic pain. These therapies help patients to develop a greater awareness of their bodies, learn to accept their pain without judgment, and engage in meaningful activities despite their pain.
Non-Opioid Medications: Pharmacological Alternatives for Pain Management
While opioids may be an effective treatment for acute pain, their long-term use in chronic pain management is fraught with potential risks. Fortunately, there are several non-opioid medications available that can effectively manage chronic pain.
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve) can help with mild to moderate chronic pain. These medications are generally safe for most people when used as directed, but they should always be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider due to potential side effects.
Prescription non-opioid medications, such as certain antidepressants and anticonvulsants, can also be effective in managing chronic pain. These medications can modulate pain signals in the central nervous system and offer relief for patients with specific types of pain, such as neuropathic pain.
The Role of Patient Education and Self-Management
Empowering patients through education and promoting self-management is a cornerstone of chronic pain management. Patients who understand their condition, treatment options, and potential risks are better equipped to make informed decisions about their care.
Self-management strategies can include a variety of activities, such as regular physical activity, relaxation exercises, and maintaining a healthy diet. Additionally, it also involves learning to pace activities to prevent pain flare-ups, using pain coping strategies, and seeking support when needed.
Moreover, technological advancements have given rise to digital health tools that aid in self-management. These tools, including mobile apps and online resources, can provide essential information, track symptoms, and offer online support groups for patients dealing with chronic pain. With these resources at their fingertips, patients can play an active role in their care and have greater control over their pain management.
Remember, effective chronic pain management rarely involves a single approach. It’s often a combination of different strategies that work best. Therefore, always consult with your healthcare provider or a pain specialist to develop a comprehensive, individualized plan for managing your chronic pain.
Assistive Devices and Technology in Chronic Pain Management
In the field of pain management, assistive devices, and technology have come a long way. They offer a range of solutions to help individuals manage their chronic pain and improve their quality of life. These can be especially beneficial for those with mobility issues, arthritis, or other conditions that make movement difficult.
One such technology is Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS). This treatment uses low-voltage electrical currents to relieve pain. A TENS unit can be used to manage pain in several different ways, including blocking pain signals to the brain, stimulating the production of endorphins (the body’s natural painkillers), and improving blood circulation to promote healing.
Additionally, assistive devices such as canes, walkers, and wheelchairs can help individuals with chronic pain maintain their independence and mobility. For individuals with lower back pain, lumbar support devices or ergonomic chairs can provide relief. For those suffering from hand or wrist pain, specially designed keyboards or voice recognition software can minimize strain.
Moreover, innovative pain relief devices are continually being developed. For instance, wearable tech, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, can help monitor physical activity and sleep patterns, which can be essential factors in managing chronic pain. With these technologies, individuals can actively participate in their pain management and foster a greater sense of control over their condition.
Conclusion: A Multidisciplinary Approach to Chronic Pain Management
In conclusion, managing chronic pain without opioids is a challenging but attainable goal. By embracing a multidisciplinary approach, individuals can explore a variety of proven strategies that offer effective pain relief without the risk of addiction or other serious side effects associated with opioid medications.
Physical therapy, integrative therapies, psychological interventions, non-opioid medications, patient education, self-management, and the use of assistive devices and technology all play crucial roles in chronic pain management. These strategies can be tailored to an individual’s specific needs and preferences, fostering a sense of autonomy and empowerment.
As our understanding of chronic pain continues to evolve, so does our approach to managing it. The emphasis has shifted away from a purely medication-based approach to a more holistic one, considering the physical, psychological, and emotional aspects of pain. This shift is not only changing how we treat chronic pain but also how we perceive it.
Ultimately, the most effective strategy for managing chronic pain is a patient-centered approach, where the individual is actively involved in their care and the goal is not just pain relief, but also improving overall quality of life. As more research is conducted and more treatments are developed, there is hope for a future where chronic pain can be managed more effectively, enhancing the lives of those who live with it every day.
Remember, always consult with your healthcare provider or a pain specialist to develop a comprehensive, individualized plan for managing chronic pain.